20 Green Sand Casting Defects and Their Suggested Remedies
- Hill and Griffith

- Sep 24, 2019
- 1 min read
Originally published January 2017 by Mechanical Engineering
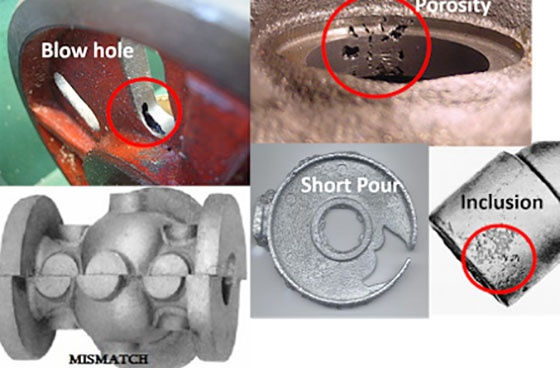
Probable causes and suggested remedies of various casting defects such as blow holes, shrinkage, porosity, misruns, hot tears, mental penetration, cold shuts, cuts and washes, inclusions, fusion, drops, shot metal, shift, crushes, rat-tails, swells, hard spot, run out, fins and fash, spongings and warpage are given in the below table.

Photo credit: Green Mechanic
S.no | Name of Casting Defect | Probable Causes | Suggested Remedies |
1 | Blow holes |
|
|
2 | Shrinkage |
|
|
3 | Porosity |
|
|
4 | Misruns |
|
|
5 | Hot Tears |
|
|
6 | Mental penetration |
|
|
7 | Cold shuts |
|
|
8 | Cuts and washes |
|
|
9 | Inclusions |
|
|
10 | Fusion |
|
|
Read more about the next 10 Green Sand Casting defects and their remedies at Mechanical Engineer.
More News from Mechanical Engineer




Comments